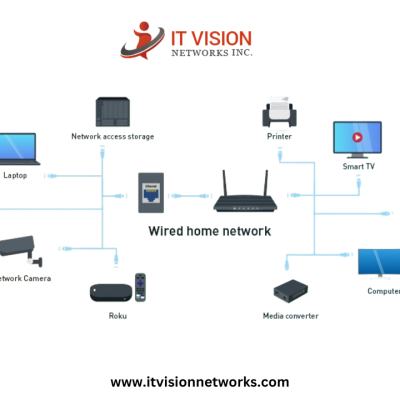
WANs (Wide area networks) are the most essential component of modern networking infrastructures, enabling organizations to connect their geographically dispersed offices, data centers, and remote users. In this article, we will delve into the world of WANs, exploring their importance, key components, types of connections, challenges in implementation, and the evolution of WAN technologies.
What is WAN (Wide area networks)
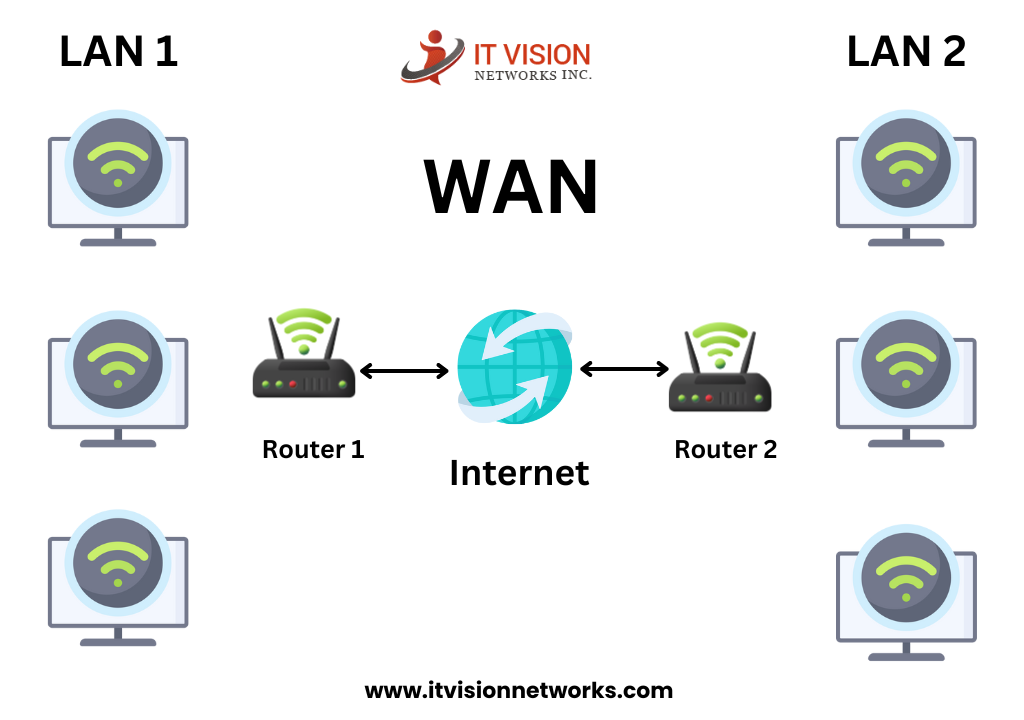
A Wide Area Network, or WAN, is a network infrastructure that spans a large geographical area, connecting multiple local area networks (LANs). Unlike LANs confined to a single location, WANs enable communication and data transfer across long distances. WANs can be established using various technologies, including traditional leased lines, MPLS networks, and the latest Software-Defined WAN (SD-WAN) solutions.
Understanding WAN and Its Importance
In today’s interconnected world, businesses rely heavily on WANs to ensure seamless connectivity between their locations. WANs enable organizations to achieve efficient data transfer, real-time communication, and collaboration across different branches. Whether a multinational corporation or a small business network solutions with remote employees, WANs provide the necessary infrastructure to connect and integrate operations. This seamless connectivity enhances productivity, accelerates decision-making, and streamlines business processes, ultimately improving customer satisfaction and competitive advantage. Critical Components of WAN Solutions
Wide Area Network solutions have several vital components that establish and maintain a reliable network infrastructure. These components include routers, switches, firewalls, and WAN optimization devices. Routers play a crucial role in directing traffic between different networks, while switches provide the necessary connectivity within a network. Firewalls ensure network security by monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing traffic. On the other hand, WAN optimization devices enhance network performance by minimizing latency, reducing data congestion, and optimizing bandwidth utilization.
Types of WAN Connections
WANs can be established using various connections, depending on an organization’s specific needs and requirements. Traditional leased lines, such as T1 or T3, provide dedicated point-to-point connections with guaranteed bandwidth. While leased lines offer reliable and secure connectivity, they can be costly and time-consuming to set up. Another WAN connection type is MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching), which uses private links to create a virtual private network (VPN). MPLS networks offer enhanced security and quality of service (QoS) but can be expensive for organizations with multiple locations.
Challenges in WAN Implementation
Implementing a WAN infrastructure comes with its own set of challenges. One of the significant challenges is ensuring consistent network performance and reliability across long distances. WAN connections can be prone to latency, packet loss, and jitter, especially when traversing public internet links. Bandwidth limitations can also impact network performance, mainly when dealing with data-heavy applications or large file transfers. Additionally, managing and maintaining WAN hardware and software components can be complex and time-consuming, requiring skilled IT personnel and dedicated resources.
The Evolution of WAN Technologies
Over the years, WAN technologies have evolved to address the challenges and inefficiencies of traditional solutions. One such game-changer in networking is Software-Defined WAN (SD-WAN). SD-WAN leverages software-defined networking principles to simplify WAN management and improve performance. SD-WAN enables centralized management, automated traffic routing, and dynamic bandwidth allocation by decoupling the control plane from the underlying hardware. This results in increased agility, cost savings, and improved application performance across the WAN.
SD-WAN: A Game-Changer in Networking
SD-WAN has revolutionized the way organizations design and manage their WAN infrastructure. Using software-defined principles, SD-WAN provides businesses with greater flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. With SD-WAN, organizations can quickly establish and manage secure connections between their locations, whether physical offices or remote sites. The centralized management and automation capabilities of SD-WAN simplify network administration, reduce manual configuration efforts, and enable efficient bandwidth utilization. Furthermore, SD-WAN can intelligently prioritize critical applications, ensuring optimal performance even in bandwidth-constrained environments.
WAN Security Strategies
When it comes to WANs, security is of utmost importance. Wide Area Network solutions should incorporate robust security measures to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. Firewalls are crucial in securing the WAN infrastructure by filtering traffic and blocking potential threats. Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) and Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) can be implemented to further enhance security by encrypting data and establishing secure connections over public networks. Additionally, WAN security strategies should include regular vulnerability assessments, patch management, and employee training to mitigate the risks of cyberattacks and data breaches.
MPLS Networks Explained
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) networks have long been famous for organizations requiring secure and reliable WAN connectivity. MPLS networks create virtual private networks by assigning labels to packets, allowing for efficient routing and prioritization. This technology offers predictable performance, low latency, and high-quality service, making it ideal for real-time data transmission applications, such as voice and video conferencing. However, MPLS networks can be costly, especially for organizations with many locations, and their deployment and management can be complex.
The Role of Leased Lines in WANs
Leased lines have been the go-to option for connecting geographically dispersed locations for many years. Leased lines provide dedicated point-to-point connections, ensuring high bandwidth and low latency. They offer a secure and reliable means of communication, making them suitable for organizations that require consistent and guaranteed connectivity. However, leased lines can be expensive, particularly for organizations with multiple locations or a need for high bandwidth. Provisioning and installing leased lines can be time-consuming and require coordination with service providers.
Cloud Integration with WAN
With the increasing adoption of cloud-based services, WANs play a crucial role in enabling seamless integration with the cloud. Cloud integration with WAN allows organizations to securely access and transfer data between their on-premises infrastructure and cloud platforms. WAN optimization techniques, such as data deduplication and compression, can improve the performance and efficiency of data transfers to and from the cloud. Additionally, WAN solutions should include robust security measures to protect sensitive data in transit and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Security Concerns and Solutions in WANs
Wide Area Networks are susceptible to various security threats, including unauthorized access, data breaches, and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. Organizations should implement a comprehensive security strategy to mitigate these risks, including firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, secure VPNs, and regular security audits. Network segmentation can also enhance security by isolating sensitive data and limiting access to authorized users. Employee awareness and training programs must educate users about best practices for security and potential threats.
Cost Considerations and ROI of WAN Implementation
Implementing a Wide Area Network can involve significant costs, including hardware, software, installation, and ongoing maintenance expenses. Organizations must carefully evaluate the costs and benefits of different WAN solutions to ensure a positive return on investment (ROI). Factors to consider include the number of locations, bandwidth requirements, security needs, and scalability. While traditional leased lines and MPLS networks may have higher upfront costs, they offer reliability and guaranteed performance. On the other hand, SD-WAN solutions provide cost savings and agility but require careful planning and consideration of network requirements.
Future Trends in WAN Solutions
The world of WAN solutions is continuously evolving to meet the changing needs of businesses. One of the future trends in WAN is the convergence of networking and security, where WAN solutions incorporate built-in security features to simplify deployment and management. Another trend is the adoption of Software-Defined WAN (SD-WAN) as the standard for wide-area networking, driven by its flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and automation capabilities. Additionally, integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) technologies into WAN solutions will enable intelligent traffic routing, predictive network analytics, and proactive security measures.
Conclusion
Wide-area network solutions are crucial for organizations seeking seamless connectivity between dispersed locations. Whether connecting physical offices, data centers, or remote employees, WANs enable efficient data transfer, real-time collaboration, and streamlined business processes. With the evolution of WAN technologies, organizations now have various options, including traditional leased lines, MPLS networks, and Software-Defined WAN (SD-WAN) solutions. By carefully considering their needs and requirements, businesses can implement a WAN infrastructure that ensures reliable connectivity, enhances security, and optimizes network performance.
FAQs
Wide area network services solutions provide organizations with the necessary tools and technologies to establish and manage their WAN infrastructure. These solutions typically include hardware, software, and support services to ensure reliable connectivity, optimal performance, and robust security.
Wide area networks (WANs) refer to network infrastructures that connect geographically dispersed locations using wired or wireless connections. Wireless wide area networks (WWANs) utilize wireless technologies like cellular networks to establish connectivity. While both WANs and WWANs serve the same purpose of connecting remote locations, WWANs offer the advantage of mobility and flexibility.
WAN solutions enhance business productivity by enabling seamless communication and collaboration across different locations. With a robust WAN infrastructure, organizations can efficiently transfer data, share resources, and access critical applications, resulting in improved decision-making, faster response times, and streamlined business processes.
Implementing WAN solutions comes with security challenges, including the need to protect sensitive data, prevent unauthorized access, and mitigate the risks of cyberattacks. Organizations must implement robust security measures, such as firewalls, VPNs, and intrusion detection systems, to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of their data across the WAN.
Organizations should carefully evaluate their needs and requirements to provide a positive return on investment (ROI) when implementing WAN solutions. Factors to consider include the number of locations, bandwidth requirements, security needs, and scalability. Organizations can achieve cost savings, improved productivity, and enhanced business outcomes by choosing the right WAN solution and optimizing network resources.
Cloud integration with WAN solutions enables organizations to connect their on-premises infrastructure seamlessly with cloud platforms. This integration allows efficient data transfer, scalability, and access to cloud-based services. WAN optimization techniques, such as data deduplication and compression, can further enhance the performance and efficiency of cloud integration.
Using technologies such as MPLS networks and SD-WAN, WAN solutions can address network performance challenges across long distances. MPLS networks offer predictable performance and low latency, making them ideal for real-time applications. On the other hand, SD-WAN provides dynamic bandwidth allocation, traffic optimization, and centralized management, ensuring optimal performance even over long distances.
The future trends in WAN solutions include the convergence of networking and security, the adoption of Software-Defined WAN (SD-WAN) as the standard, and the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) technologies. These trends aim to simplify WAN deployment and management, enhance security, and enable intelligent traffic routing and predictive analytics.